Description
Coconut is a tropical fruit from the coconut palm tree (Cocos nucifera), widely known for its versatility and nutritional value. Here’s a breakdown of its key features:
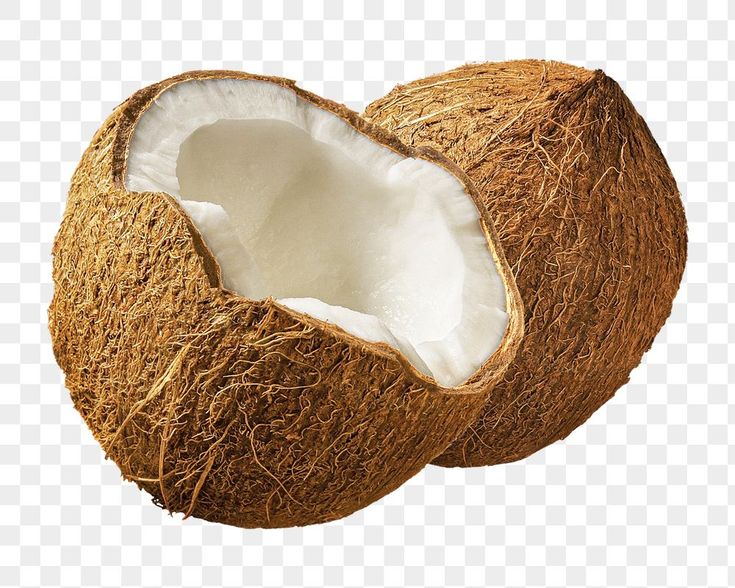
🌴 Physical Description:
-
Outer layer (exocarp): Smooth, green or yellow when immature; turns brown and fibrous as it matures.
-
Husk (mesocarp): Thick, fibrous coir that protects the inner shell.
-
Shell (endocarp): Hard, woody shell that encases the edible parts.
-
Flesh (endosperm): White, meaty interior that thickens as the coconut matures.
-
Water: Clear liquid inside young coconuts, known as coconut water.
🍽️ Culinary Uses:
-
Coconut water: Refreshing drink high in electrolytes.
-
Coconut milk/cream: Made from grated flesh, used in cooking (especially Southeast Asian, Caribbean, and Indian cuisine).
-
Desiccated coconut: Dried and shredded for baking or confections.
-
Coconut oil: Extracted from the meat; used for cooking and cosmetics.
🥥 Nutritional & Health Facts:
-
Rich in healthy fats (especially medium-chain triglycerides).
-
Contains fiber, vitamins (like B-complex), and minerals (such as manganese, copper, and selenium).
-
Coconut water is hydrating and low in calories.
🔧 Other Uses:
-
Coir fibers: Used in ropes, mats, brushes, and mattresses.
-
Coconut shells: Used as bowls, utensils, or fuel.
-
Leaves & trunk: Used in construction, crafts, and fuel in some cultures.
Coconuts are not only a vital food source in many tropical regions but also an important economic crop globally, earning them the nickname “tree of life” in some cultures.